55
If Windows won’t start, it’s annoying, but often fixable. By taking a systematic approach – from checking the hardware to safe mode and recovery options – you can find and fix the cause.
Windows won’t start anymore: Check the hardware
If your Windows operating system no longer starts, there may be various reasons for this – from hardware problems to software errors. Before you look at software solutions, you should make sure that your computer’s hardware is working properly:
- Check connections: Make sure that all cables are properly connected, especially the power cord, keyboard, mouse, and monitor. A loose cable can prevent the system from starting up.
- Power supply: If the computer does not turn on, the power supply may be defective. Test whether the socket is working by plugging in another device or using a different power cable.
- Internal components: Carefully open the case of your PC (after disconnecting it from the power supply) and check whether components such as RAM and graphics cards are firmly seated. Dust can also cause problems, so carefully clean the inside of the computer.
Start in Safe Mode if Windows has startup issues
Safe Mode loads Windows with minimal drivers and services, which can be helpful for identifying software issues:
- Accessing Safe Mode: For Windows 10 and 11, restart the computer and repeatedly press the F8 key during startup until the “Advanced Boot Options” menu appears. Select “Safe Mode” from there.
- Troubleshooting in Safe Mode: Uninstall recently installed programs or drivers that may be causing conflicts. It also makes sense to run a full virus scan to rule out malware as a cause.
Using Windows recovery options
If Safe Mode doesn’t help, you can use the following recovery options:
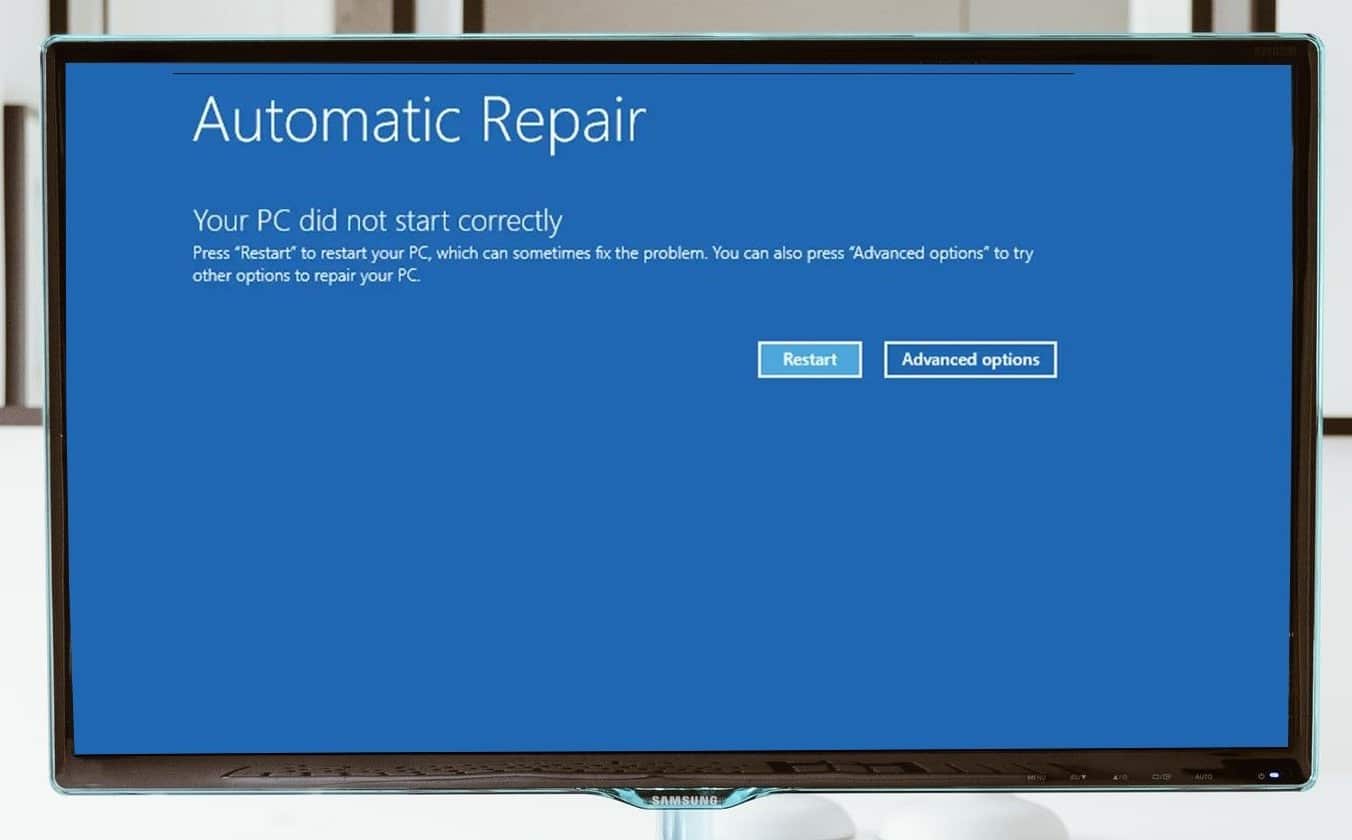
- Automatic Repair: For Windows 10 and 11, restart the computer and interrupt the startup process twice in a row (e.g. by turning off the PC during booting). If Windows detects problems during the third start attempt, it will automatically switch to “Automatic Repair”. There you can get to “Troubleshooting” via “Advanced Options” and then select “Startup Help”.
- System restore: Using a restore point: If you have previously created a restore point, you can restore your system to that state. To do this, go to “Advanced options” ☻ “Troubleshoot” ☻ “Advanced options” ☻ “System restore” and follow the instructions.
- Reinstalling Windows: Before reinstalling Windows, you should back up important data. You can do this, for example, with a live CD or a bootable USB stick.
- Installing Windows: Use an installation disk (USB stick or DVD) with the appropriate version of Windows. Boot from it and follow the instructions for reinstalling.