701
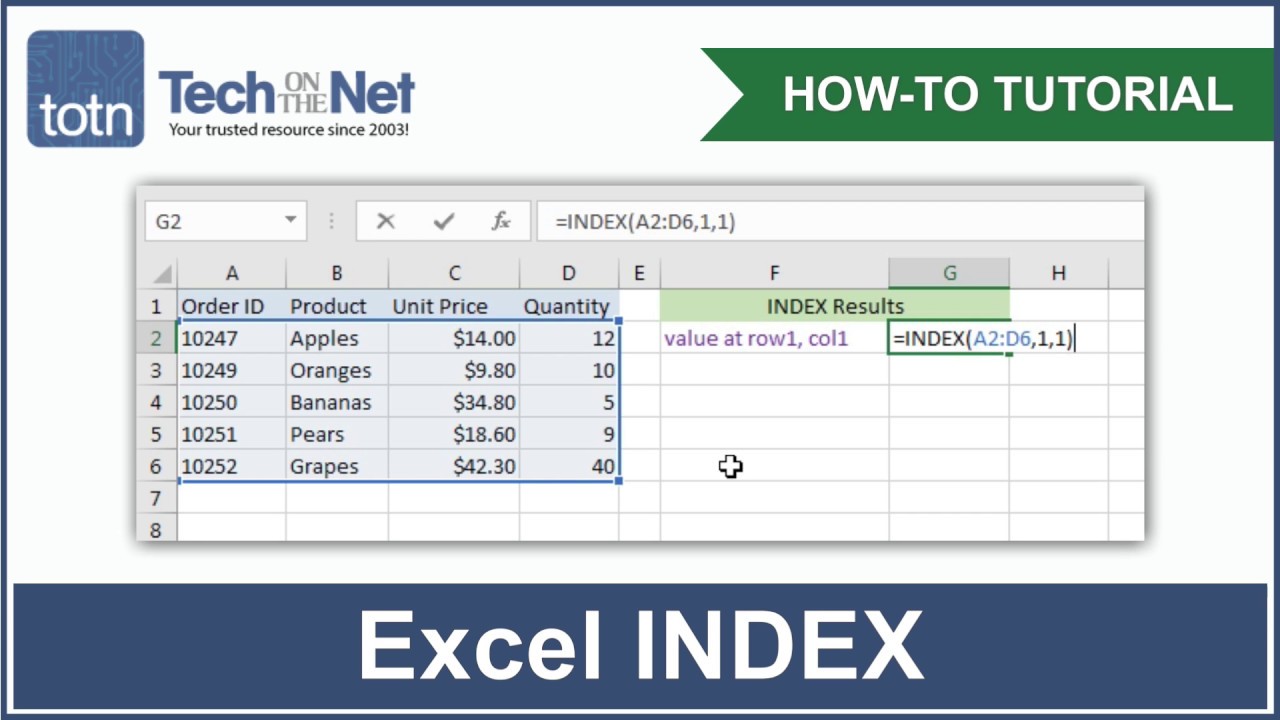
Excel offers an index function to access data from tables and sub-tables. It provides the value of a cell at a specific position.
Using the index function in Excel
Excel is a spreadsheet program. You can access individual entries in a table using the combination of row and column. You can create several sub-tables in a table. You can use the index function to retrieve values from these sub-tables. We will explain how this works using the example of the GbR flower shop.
- The flower shop GbR has an Excel document with the table “Statistics” and the subtable “Working hours” (red).
- The list of employees forms the rows of the sub-table, a list of weekdays the columns. The working hours per employee and day are entered (yellow).
- Use the index command to find out which employee worked how long on which day of the week. The Excel function looks like this: “=INDEX(Table;Row;Column)”, so “=INDEX(WorkingHours;EmployeeList;WeekdayList)”.
The Excel comparison function
The index function is particularly useful in combination with the comparison function. This can save you counting the desired row and column.
- Enter the name of the desired employee in a cell. Alternatively, you can also select the employee name using a drop-down menu.
- In another cell, you can determine the row that corresponds to the row in the sub-table. To do this, enter “=VERGLEICH(employee;employee list;0)”. The row number that corresponds to the name is displayed (yellow).
- Proceed in the same way with the weekday and column number (green).
- If you now use the index function, you can import the numbers output using the comparison function (blue).