1.1K
MRI and CT are common diagnostic tools in medicine, but they have certain differences. What the methods are used for is explained here.
Difference MRI and CT: MRI diagnosis explained simply
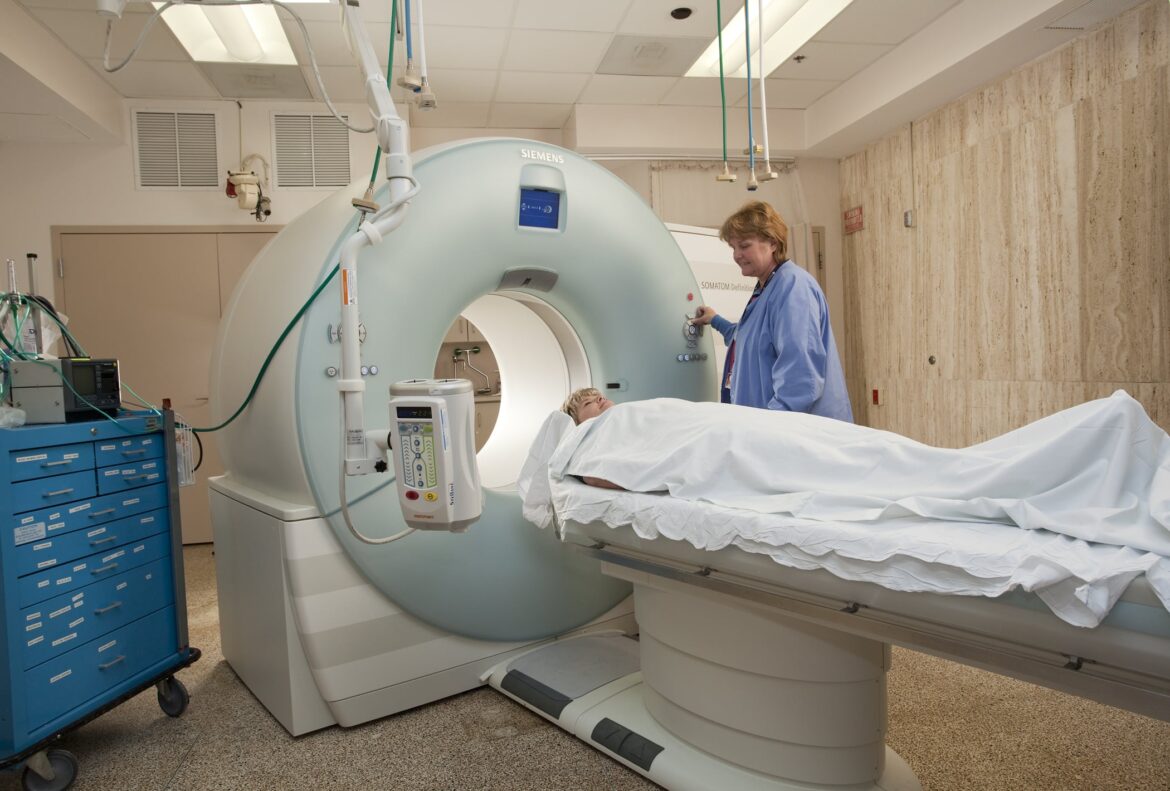
Most patients associate an MRI examination with an unpleasant, lengthy and, above all, noisy examination. Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, works by using a magnetic field. During the 15-20 minute examination, the patient lies in a tube. This is how magnetic resonance therapy works:
- The patient is placed on a couch. This couch is then slid into the magnetic resonance scanner. If necessary, the patient is given a so-called contrast medium before the examination, which makes it easier for the doctors to evaluate the image later.
- The examination itself takes between 15 and 20 minutes. During the examination, the patient hears the knocking sounds typical of an MRI scanner.
- With this magnetic field, the tomograph “scans” the body and in particular the patient’s organs layer by layer.
- The diagnostic option MRI is used by doctors especially when organs are to be examined.
- According to experts, one advantage of this technology is that, in contrast to CT examinations, no harmful X-rays are used.
The CT method simply explained
Computed tomography, or CT for short, works in contrast to MRI diagnostics with X-rays. During the examination, the patient is also on a couch and in a machine. However, the duration of the examination is much shorter.
- Contrast media are also sometimes used in CT examinations. After administration, the patient lies down on a couch that is pushed into the CT scanner.
- The machine now carries out the examination using X-ray technology. The difference between this and a conventional X-ray examination is that with a CT the whole body is “scanned”.
- During the examination, which usually only takes a few minutes, the tomograph rotates around the patient to capture every view of the body.
- The cross-sectional images taken are now computer-assisted to form a 3D image.
- Computed tomography offers the advantage of a rapid examination and is therefore often used in emergency medicine. In addition, this form of diagnosis is particularly suitable for imaging the human skeleton.
- The disadvantage of CT is the use of X-rays, which can sometimes have a harmful effect on the human organism.
The harmful effects of X-rays in CT
Although CT offers many benefits, it is important to be aware of the potential harmful effects of X-rays.
- X-ray radiation is a high-energy form of electromagnetic radiation. It penetrates tissue and produces images by being absorbed by the various structures in the body. Although the radiation dose during a CT scan is relatively low, repeated exposure to X-rays over time can pose health risks.
- One of the main concerns with the use of X-rays is the potential damage to genetic material. X-rays are energetic enough to ionise the DNA in cells.
- It is important for doctors and radiologists to weigh the potential risks of X-rays when deciding to have a CT scan. In some cases, the benefits of an accurate diagnosis may outweigh the risks of radiation exposure.