The definition of markup is important for effectively structuring and designing documents and websites. In the Internet age, we encounter it almost everywhere. In this article, you will learn exactly what markup means and how it is used in the digital world to optimally display content.
Markup definition: What you need to know
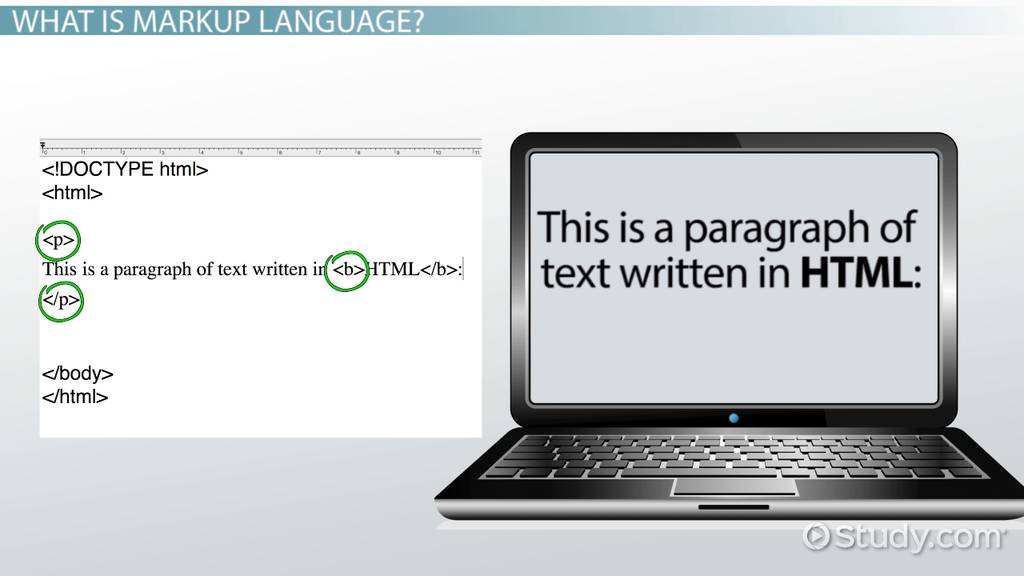
Markup is a term that is frequently used in the context of information processing. Essentially, it is a language or system used to format and structure text documents. The best-known markup language is HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), which forms the backbone of the World Wide Web.
- Markup refers to the use of markup elements to give a document structure and format. These elements often consist of tags that mark the beginning and end of a format, such as for bold text.
- Markup originated in the publishing industry, where it was used to prepare manuscripts for printing. Today, its use has expanded, especially in the digital world.
- HTML is the most widely used markup language and is used to create web pages. It allows developers to organize and present text, images, and other media.
- In addition to HTML, there are other markup languages such as XML (Extensible Markup Language) and LaTeX, each of which offers specific areas of application and advantages.
Technical guide: How markup works
Understanding how markup works is crucial to understanding its applications. Tags and attributes can be used to highlight or treat certain parts of a document separately. This not only enables visual design, but also allows the data to be processed by machines.
- In a typical HTML file, the content is structured by a variety of elements. Each element begins with a start tag and ends with an end tag, with the actual content in between.
- Tags can contain attributes that provide additional information, such as the width of an image or the color of text. This flexibility makes the language extremely versatile.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is often combined with HTML to control the layout and design of web pages. While HTML provides the structure, CSS takes care of the visual design.
- The markup language also allows interaction with scripting languages such as JavaScript, making web pages dynamic and interactive. It thus forms the basis for many modern web applications.