7
When buying a screen for your PC, you should pay attention to the diagonal size and resolution of the monitor.
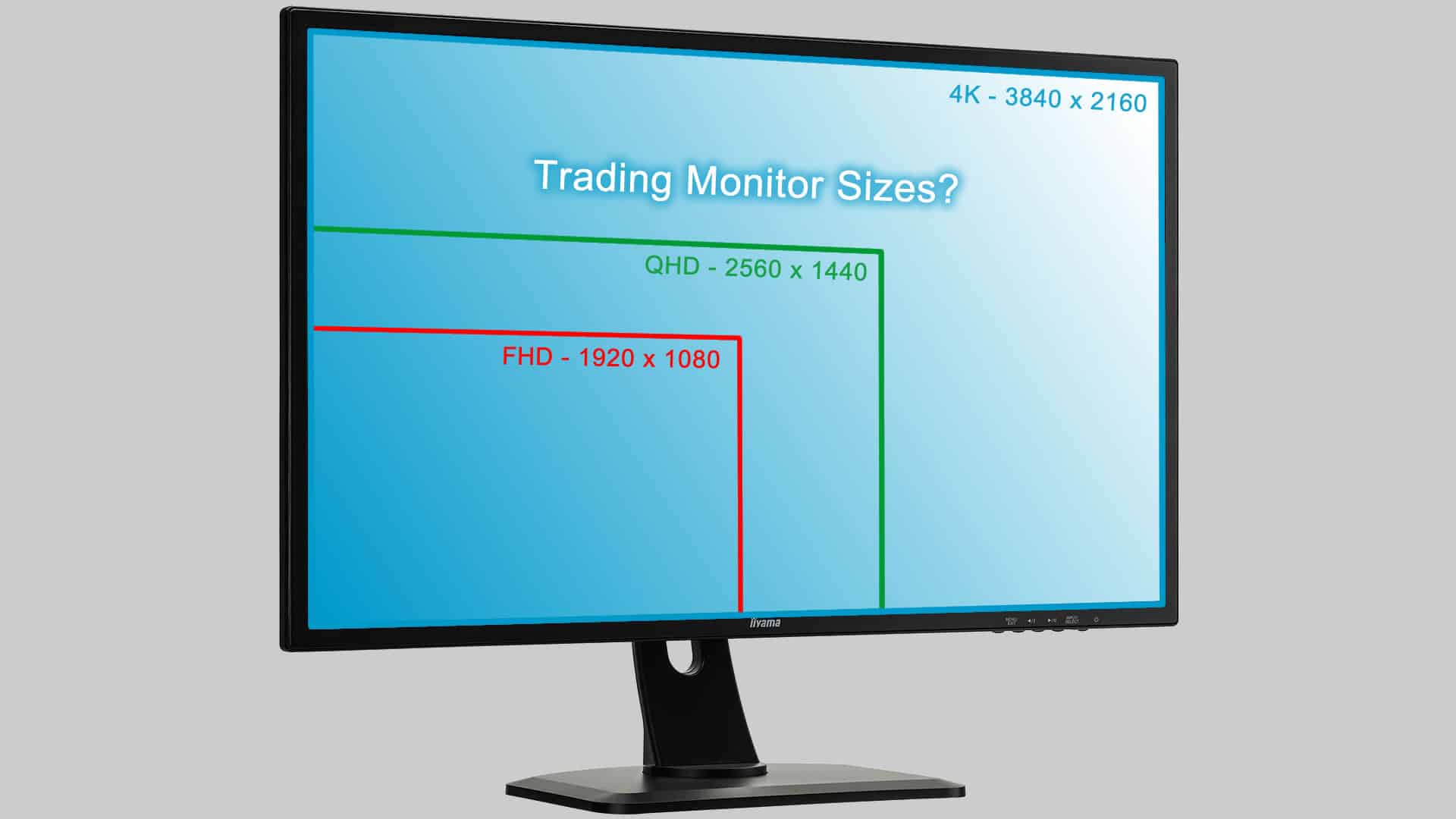
Monitor size/diagonal: It’s all about the resolution
The largest screen is of little use if the resolution is too low. The resolution indicates how many pixels the screen can display. It not only affects the image quality, but also how much space is available on the screen for program windows. Current standards for monitor resolutions are:
- Full HD (1920 x 1080 pixels): Full HD is still the minimum standard for new PC monitors. It is particularly suitable for smaller screens up to 24 inches (approx. 61 cm). However, Full HD can appear less sharp on larger screens because the pixel density (pixels per inch, PPI) decreases.
- QHD or WQHD (2560 x 1440 pixels): This resolution is often used for monitors between 27 and 32 inches. It offers greater sharpness and more space for content. QHD is ideal for gaming, video editing, or CAD applications.
- 4K monitors (3840 × 2160): Screens with 4K resolution place high demands on the graphics card, especially for gaming or demanding applications. High-end graphics cards are required for smooth working or gaming in 4K. For games with high FPS and maximum detail, a powerful processor and sufficient RAM are also necessary to avoid bottlenecks.
- Ultrawide monitors (21:9) with UWQHD resolution: Ultrawide monitors with UWQHD resolution (3440 × 1440) offer a wider field of view than conventional monitors in 16:9 format. They are ideal for multitasking, as multiple windows can be displayed side by side. These monitors are particularly popular with gamers for immersive gaming experiences and with professional users for video editing or CAD applications.
- Size and resolution: Full HD looks sharp on smaller screens (e.g., 24 inches) because the pixel density is high. On larger monitors (27 inches and above), Full HD can appear pixelated because the same number of pixels are spread over a larger area. For monitors 32 inches and above, higher resolutions such as QHD or 4K UHD are recommended to ensure a sharp display.
- Processing power for higher resolutions: Screens with higher resolutions (e.g., QHD or 4K) require more processing power from the graphics card. Especially when gaming or editing videos, you should make sure that the hardware is powerful enough to display content smoothly.
- Important: Pixel density (PPI), screen size, and viewing distance are closely related and affect the perceived image quality and comfort when using a monitor. Therefore, choosing the right monitor depends on the balance between pixel density, screen size, and viewing distance.
- For smaller monitors (27 inches), WQHD or 4K are recommended to ensure high sharpness. The ideal viewing distance should be adjusted to the resolution: the higher the resolution and pixel density, the closer you can sit without noticing pixels.
Screen size: These are your options for diagonal screen size
The choice of monitor size depends largely on the intended use. The screen diagonal is measured in inches, with one inch corresponding to 2.54 centimeters. Here are the most common sizes and their ideal applications:
- 17 inches (43.18 cm): This used to be the standard size for office applications and surfing the Internet. The resolution is usually 1280 x 1024 pixels. This size is no longer up to date, as it offers little space for multitasking and the pixel density is low compared to more modern monitors.
- 19 inches (48.26 cm): This size is slightly larger than 17 inches and easier on the eyes thanks to the larger font size. The resolution is also often 1280 x 1024 pixels. This size is also outdated and hardly used anymore.
- 22 inches (55.88 cm): You have more space on a 22-inch monitor with 1680 x 1050 pixels. A comfortable size for working at a desk. However, this size is often too small for modern applications such as gaming or multitasking.
- 24 inches (60.92 cm): Full HD is usually available from 24 inches. With 1920 x 1080 pixels, you have enough space for multitasking. Two windows can be conveniently placed side by side. 24 inches is also a good choice as a gaming monitor. Advantage: Two windows can be conveniently displayed side by side. Popular with gamers and for home office applications.
- 27 inches (68.58 cm): If you like it a little bigger, go for a 27-inch monitor. Here, resolution is the key. With Full HD (1920 x 1080 pixels), the individual pixels are visible when you look closely. The 2560 x 1440 pixels are worth it here. Ideal for users who need more space or want to enjoy immersive games.
- 30 inches and above: Screens with 30 inches and above usually only make sense for professional applications such as Photoshop, video editing, or CAD programs. Such applications can be used optimally on a large monitor with high resolution. For gaming, you can also consider 4K resolution at this size. Recommendation: For monitors of this size, a high resolution such as 4K is necessary to ensure a sharp display. Particularly useful for designers and gamers.